ERCP & CBD Stone Removal
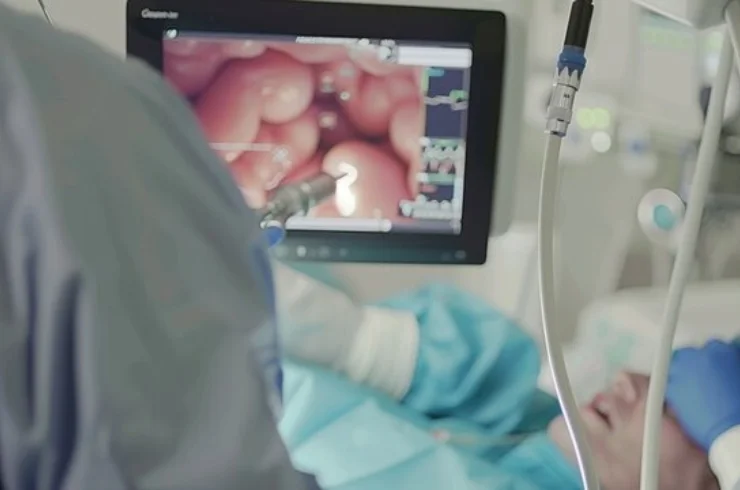
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy (X-ray) to examine and treat conditions of the bile ducts, pancreatic duct, and gallbladder. ERCP is commonly used for diagnosing and managing problems related to the bile ducts, including bile duct stones (CBD stones), blockages, and other conditions such as strictures or tumors.
Indications for ERCP:
- Bile Duct Stones (CBD Stones): These are stones that form in the common bile duct, often as a complication of gallstones. They can cause pain, jaundice, pancreatitis, or infections like cholangitis.
- Obstruction of the Bile Ducts: Due to strictures (narrowing), tumors, or scarring.
- Pancreatitis: Particularly when caused by a stone blocking the pancreatic duct.
Procedure:
Preparation: The patient is usually sedated or given general anesthesia. A flexible endoscope (a tube with a camera and light) is inserted through the mouth, down the esophagus, and into the stomach and duodenum (first part of the small intestine).
Accessing the Bile Duct: A small catheter is threaded through the endoscope into the ampulla of Vater (where the bile duct and pancreatic duct meet in the duodenum).
Injection of Contrast Dye: A contrast medium is injected into the bile and pancreatic ducts, and X-ray images are taken to visualize blockages, stones, or other abnormalities.
Stone Removal (CBD Stone Removal): If stones are present, they can be removed using various techniques:
- Basket Extraction: A small wire basket is used to capture and remove the stones.
- Balloon Dilation: A balloon is inflated to widen a narrowed duct and facilitate stone removal.
- Sphincterotomy: A small incision is made in the sphincter of Oddi (the muscle controlling the flow of bile and pancreatic juices into the duodenum) to allow easier removal of stones.
- Lithotripsy: In cases where the stones are large, they may be broken into smaller pieces using mechanical or electrohydraulic lithotripsy before removal.
Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, patients are monitored for complications such as bleeding or infection. The recovery time is generally short, with most patients discharged within a day or two, depending on their condition.
Risks and Complications:
While ERCP is a relatively safe procedure, some risks include:
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, a known complication of ERCP.
- Infection (Cholangitis or Pancreatitis): Though antibiotics are often given to reduce the risk, infection is still possible.
- Bleeding: Especially if a sphincterotomy is performed or if there are large stones.
- Perforation: A rare but serious complication where a hole is made in the digestive tract.
- Stone Retention: In some cases, stones may not be fully removed or may require additional procedures.
Advantages of ERCP:
- Minimally Invasive: ERCP allows for the removal of CBD stones without the need for surgery, making it less invasive and reducing recovery time.
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic: ERCP can both diagnose and treat problems simultaneously, providing immediate relief from conditions like bile duct obstruction.
In summary, ERCP is a powerful tool in diagnosing and treating bile duct stones, with the ability to remove stones and alleviate blockages or other issues in the biliary system. It’s an essential procedure in managing conditions that affect the bile and pancreatic ducts, significantly improving patient outcomes.